So, you've been using your Mac computer to execute several resources demanding operations. But have you ever wondered what's really going on under the hood?
Well, it's important you keep track of processes running on your Mac, as it can be valuable for troubleshooting, optimizing performance, and ensuring your system's stability.
In today’s post we will explore all you need to know about Mac processes. From the list of Mac processes to step-by-step instructions on how to view running processes on Mac using different effective methods.
Part 1: What Are Mac Processes?
Mac processes are the various tasks and applications that are actively running on your system. These processes consume system resources such as CPU power, memory, and disk space, and if many are running simultaneously, it can lead to a slowdown in performance and potentially cause system instability.
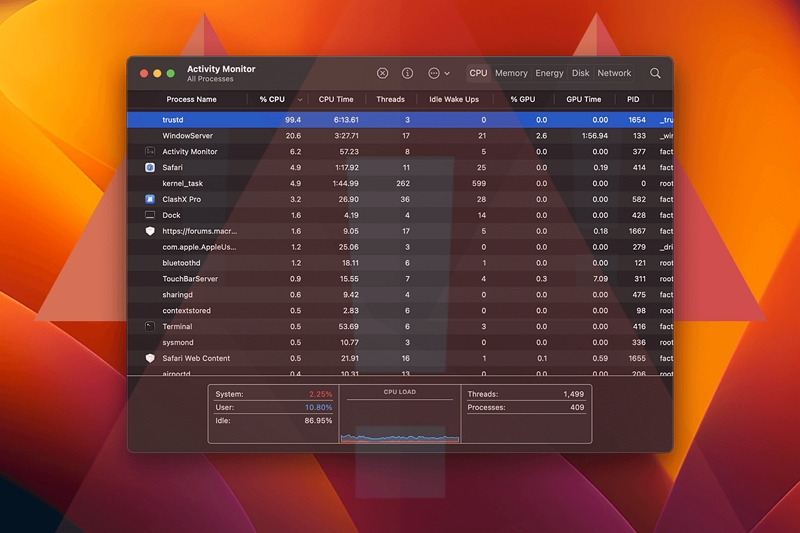
Don't know what processes run on your Mac system? Below is a list of them:
- kernel_task: The core of the operating system that manages system resources.
- WindowServer: This is a process that manages the graphical user interface and windowing system.
- Finder: The file manager and graphical user interface shell.
- Dock: Controls the macOS Dock, where app icons are located.
- SystemUIServer: Manages menu bar items, including the clock, battery, and system status icons.
- mds and mdworker: These processes are part of the Spotlight search indexing and file metadata system.
- Safari or other web browsers: Each open tab or window in your web browser runs as a separate process.
- Mail: If you use the Apple Mail app, it runs as a separate process.
- Messages: The Messages app runs as a separate process for sending and receiving messages.
- Siri: The voice assistant has its own process.
- iTunes or Music: If you use these apps for music or media playback, they have their own processes.
- Photos: The Photos app has a dedicated process for managing your photo library.
- Time Machine: If enabled, Time Machine runs as a background process for backups.
- Spotlight: The system search process that indexes files for quick searching.
- Control Center: Manages system settings and toggles accessible from the menu bar.
- Notification Center: Handles notifications and alerts.
- Bluetooth and Wi-Fi: Processes related to managing wireless connections.
- Keychain Access: Manages secure storage of passwords and keys.
- Kernel Extensions: Various kernel extensions and drivers for hardware and software.
- SecurityAgent: Handles authentication and security-related tasks.
- Location Services: Processes that manage your device's location services.
- Activity Monitor: While not a process itself, the Activity Monitor app allows you to view and manage running processes.
- Terminal: If you open the Terminal app, it runs its own shell process.
Part 2: How To See What Processes Are Running On Mac
Whether you're looking to check processes to see the top things that are consuming your system resources, to fix an issue, or more, there are several techniques you can use to execute the operation. You can check it either via “Activity Monitor” or by using “Terminal and Command” line. We've explained how to use each of these methods below.
Method 1: Use Activity Monitor
One of the most effective tools to view and manage running processes on a Mac is the Activity Monitor. This built-in utility provides a comprehensive overview of all the processes running on your system. To check processes running on Mac via Activity Monitor, follow these steps:
Step 1. Open Finder from the Dock.
Step 2. Go to “Applications” > “Utilities” and double-click “Activity Monitor”.
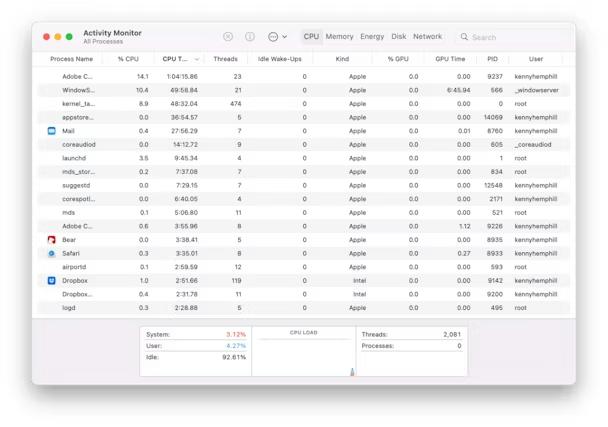
Step 3. Once Activity Monitor is open, you will see a list of processes in the main window. By default, the processes are sorted by CPU usage, but you can also sort them by other criteria such as memory usage or energy impact. You can identify specific processes by their name and monitor their resource consumption in real time.
Method 2: Use the Terminal and Command Line
The Terminal utility on Mac can also come in handy to view the Mac running processes in real-time. However, this method requires the use of command lines to be able to operate. So, you need to exercise caution when using this method, as any slight error can forcefully terminate critical system processes and can lead to system instability.
Follow the steps outlined below to view Mac running processes using Terminal:
Step 1. Open Spotlight by pressing Command + Space.

Step 2. Type "Terminal" and press Enter to launch it.
Step 3. In the Terminal window, type "Top" to see a real-time list of processes running on your Mac.
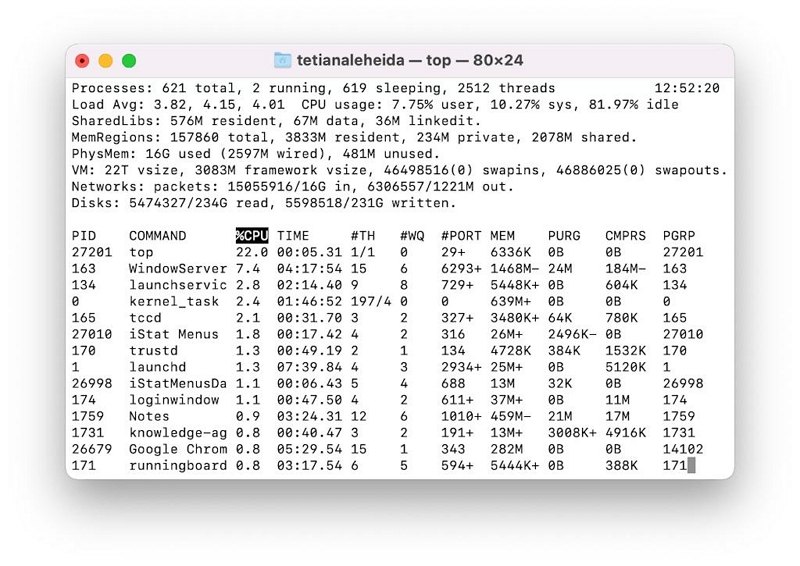
- You can sort the processes by CPU usage by typing: top -o cpu or by the memory they’re using by typing: top -o size.
Step 4. Use the arrow keys to navigate through the list and press "q" to exit the top command. You can also use the "kill" command followed by the process ID to terminate a specific process.
Part 3: Best Way To Keep Mac Overall Processes Running Smoothly and Performance
To ensure that your Mac system processes are running smoothly, it is important to perform regular cleaning. Yes, this is because unnecessary files and clutter can accumulate on system storage, consuming valuable resources and impacting performance. This is where a reliable Mac cleaning tool like Macube Cleaner can be of great help.
Macube Cleaner is a fully functional cleaning and optimization tool designed specifically for Mac users to manage their Mac storage and enhance performance. With its smart algorithm and comprehensive feature set, this tool allows you to efficiently clean your Mac's storage, remove junk files, and optimize system performance within a few clicks.
Key Features
- Removes unnecessary files, caches, logs, and other clutter that can slow down your Mac using a smart algorithm.
- Identifies and removes duplicate files, freeing up valuable disk space.
- Safely cleans your browsing history, cookies, and other sensitive data to protect your privacy.
- Helps you uninstall unwanted applications completely and securely.
- Manages startup items to improve boot times and overall system performance.
Steps to Clean Your Mac Using Macube Cleaner
Step 1. Start Macube Cleaner on your Mac and navigate to the left pane. Then, select “Smart Scan” and click on the “Scan” button.
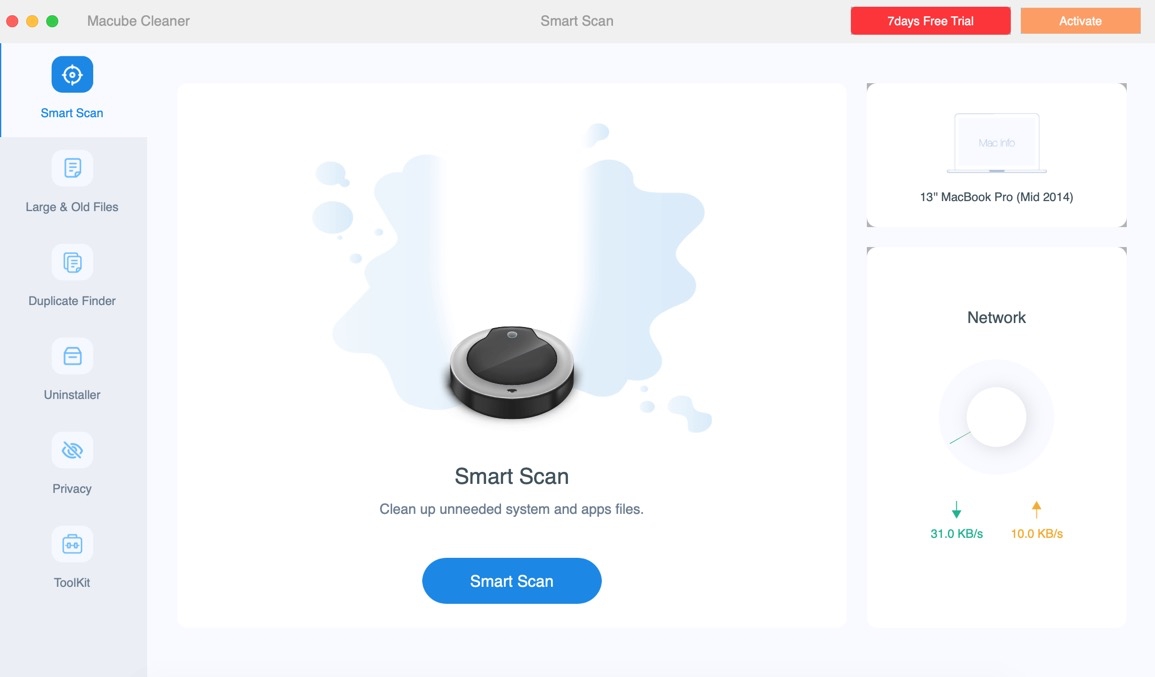
Step 2. As soon as you hit the scan button, Macube Cleaner will start to perform a deep scan on your Mac to find junk like message history, cache files, iTunes, cookies, and lots more. All of them will be displayed on your screen according to their respective categories.
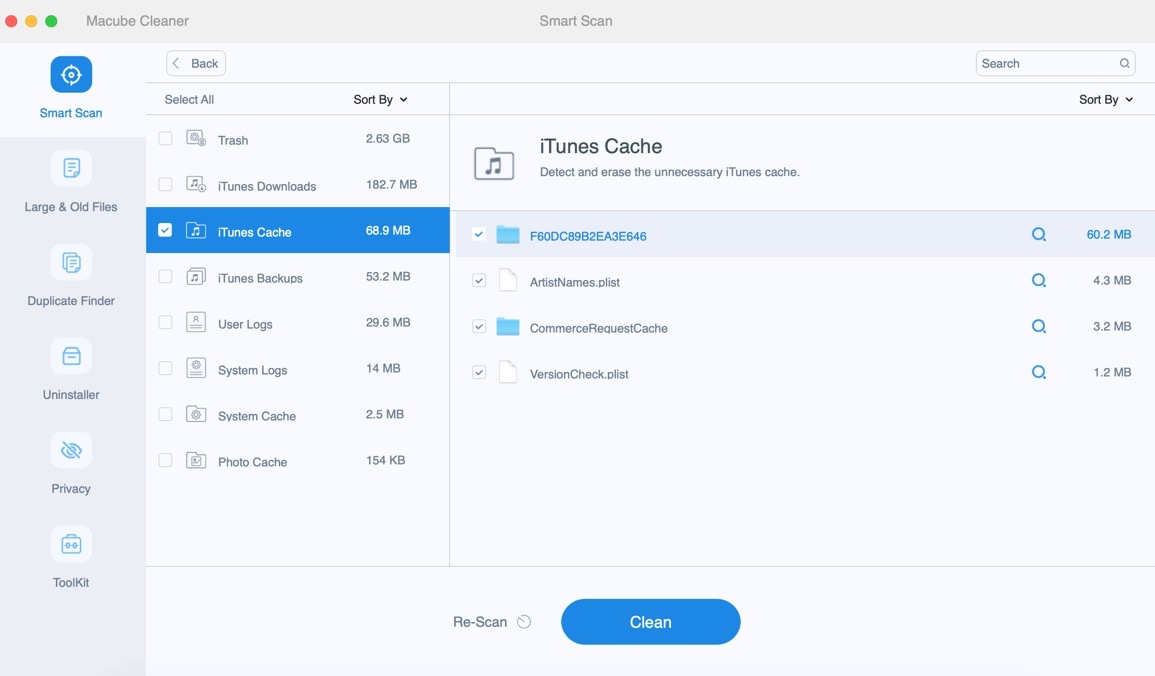
Step 3. You can “Preview” the detected junk files by clicking on the “Magnifying glass” next to them.
- After that, select the files you want to delete and on “Clean” to remove them from your Mac completely.
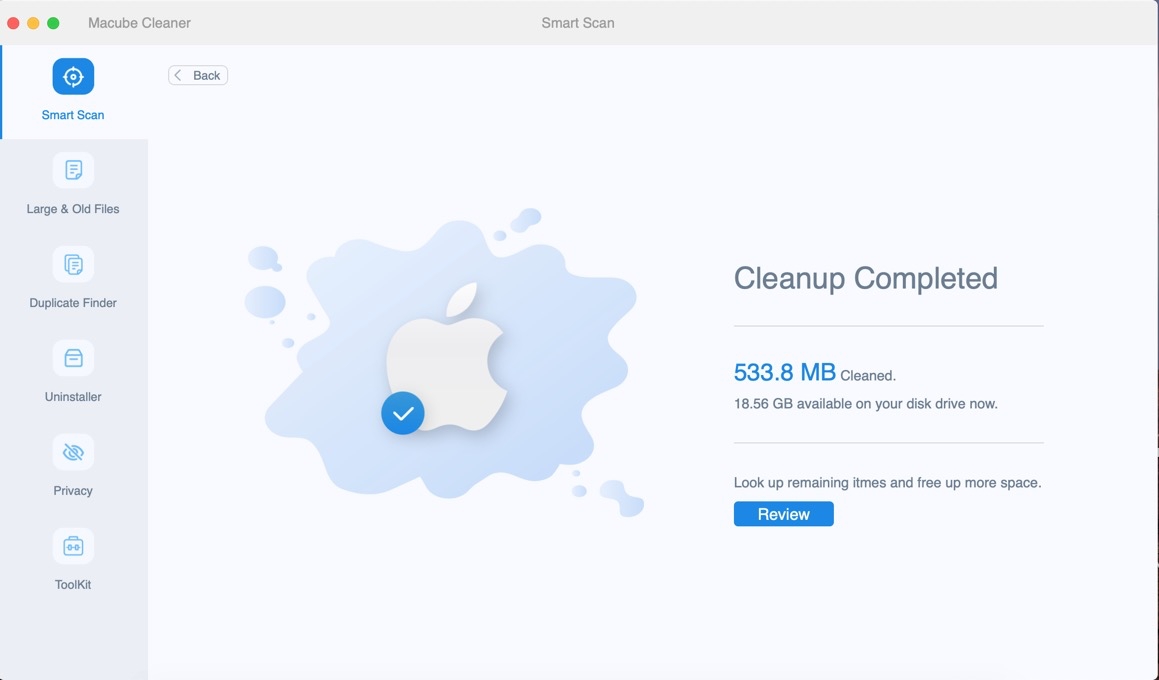
FAQs
Q: How Do I See What Programs are running on Mac?
You can see what programs are running on your Mac by checking the Dock, or using Activity Monitor or Terminal to get a detailed view of all running processes.
Q: What is the shortcut to show running processes on Mac?
The shortcut to show running processes on a Mac is Command + ALT + ESC. This shows you a list of all applications and programs currently running in your system’s background.
Conclusion
Understanding how to view and manage running processes on your Mac empowers you to maintain a smooth and efficient system.
Fortunately, you can use the power of built-in utility like Activity Monitor and Terminal commands to identify resource-hungry applications, troubleshoot system issues, and optimize your Mac's performance. You can also employ advanced software like Macube Cleaner to ensure your Mac processes are running smoothly.

Macube Cleaner
Speed up and troubleshoot your Mac super easily with a Macube full-featured free trial!
Start Free Trial