In the realm of digital landscapes, where software and hardware coalesce to power our devices, a silent witness captures every interaction, every error, and every triumph. This silent observer is none other than the system log – a record that unveils the inner workings of our MacOS-based machines.
System logs are not mere annotations; they are the breadcrumbs that lead us to understanding and resolution. System logs serve as the backstage pass, granting us access to the heartbeat of this digital orchestra. These logs span various categories, from application events to security breaches, each holding vital clues to the intricate dance of our systems.
We'll embark on a thorough investigation of MacOS system logs throughout this manual. We'll provide you the tools you need to analyze logs effectively, decipher their hidden messages, and translate their revelations into workable solutions. We'll employ techniques like using the Console app and Event Viewer, utilizing terminal commands, and interpreting log entries along the way. So let's start exploring your Mac's digital journal of adventures.
Part 1: Understanding MacOS System Logs
A. Delving into MacOS System Logs
MacOS keeps track of all of its activities, events, and communications with hardware and software components in log files called system logs. These logs act as a thorough historical record of all activities taking place behind the scenes of the user interface. Error messages, warnings, user actions, program launches, hardware detections, network activity, and security-related events are just a few of the many types of information that they cover.
System logs are important for diagnosing problems since they serve as a forensic tool for investigation and problem-solving. System logs serve as a digital trail when a bug, error, or unusual behavior happens, allowing technicians and users to go back and figure out what went wrong. Experts can establish the exact sequence of events that caused the issue and come up with workable solutions by looking at the logged events and trends. The capacity to decipher the complexity of system behavior and guarantee the stability, security, and peak performance of MacOS-based systems is made possible by the system logs.
B. Types of System Logs
To cover many facets of the system's operation, MacOS generates a variety of system logs. On MacOS, some typical categories of system logs are as follows:
- Application logs: These logs keep track of the actions and mistakes made by the apps that are operating on the system.
- System logs: Hardware detections, startup and shutdown procedures, kernel-related operations, and other general system events are all recorded in the system logs.
- Security logs: Security logs keep track of events relating to firewall activity, authorisation attempts, and other security-related activities.
- Kernel Logs: The operating system's brain is the subject of kernel logs.
- Network logs: These logs record operations involving networks, including data transfers, network connections, and adjustments to network setup.
- Diagnostic Logs: To assist in the identification of specific problems, several system components produce detailed records known as diagnostic logs.
C. Is it safe to delete mac system logs?
On a Mac, manually deleting system logs is typically not advised unless you are really knowledgeable about what you're doing. System logs are crucial for problem-solving and preserving your system's general health. Randomly deleting logs could make it more difficult for you to solve issues. You can use Macube to identify unnecessary or outdated logs and cache files that can be safely removed without causing harm to your system's functionality.
System clutter, caches, and logs can all be cleared at once by Macube. By deleting excessive cache, Macube enables you to swiftly access programs and services. The app cache needs to be deleted since using Mac programs creates a lot of unnecessary files and takes up a lot of storage space. Macube can assist you in deleting the app cache. The Smart Scan of Macube is able to offer you the greatest cleanup experience with speedy scanning, potent cleaning, and excellent security by optimizing the algorithm to an industry-leading level. And Macube is dedicated to improving the outcome at all times. To free up Mac space, which macube helps with, delete the all kinds of junk files, system junks, duplicate files, protects privacy and much more!
Main Features:
- Single-Click System Storage Release
- Can ensure that you have the greatest cleanup experience possible because to its speedy scanning, effective cleaning, and excellent security.
- Use Macube to safely empty the trash and make room.
- Free 7-day trial with all features.
- Eliminate unnecessary files to clear up disk space by using Macube to find out all the cache and attachments in the email.
Steps to recover:
Step 1: To find garbage files throughout your Mac, select Smart Scan.
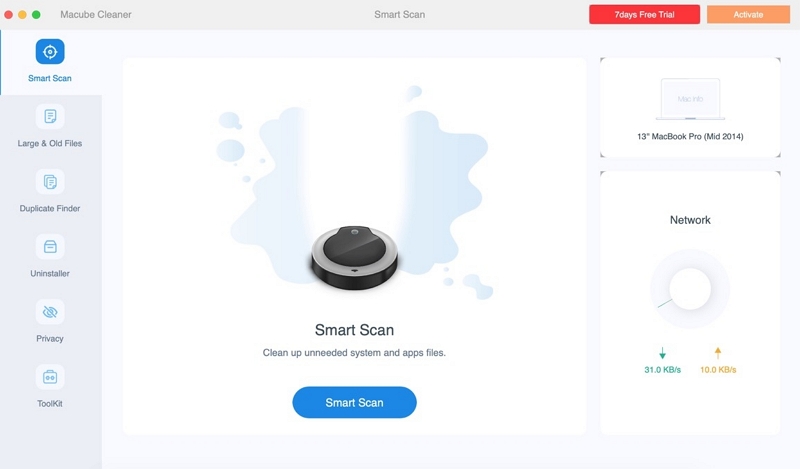
Step 2: Review the scanning findings and choose the files that are unnecessary.
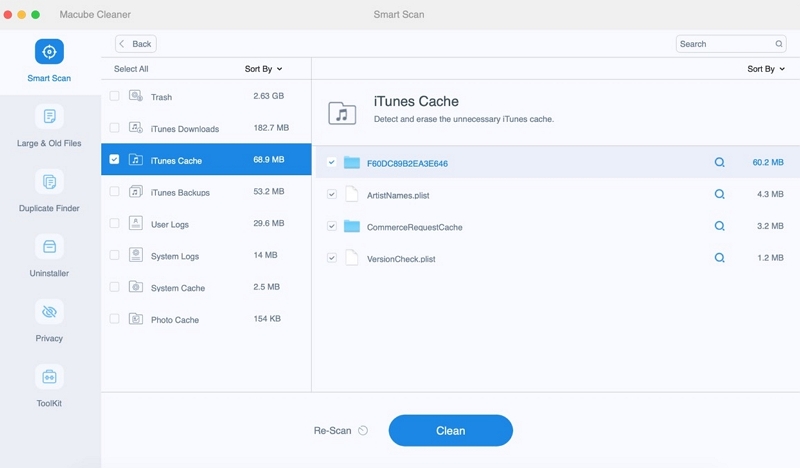
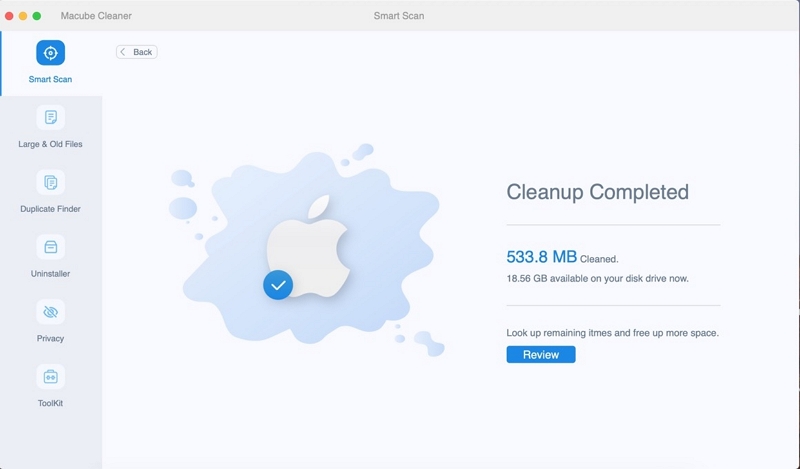
Step 3: Delete the unnecessary files with a single click to save up disk space.
Part 2: Accessing MacOS System Logs
System logs can be seen and examined graphically using the Console program on MacOS. Here's how to get to it:
Step 1: Launch the Console program
The Console program is located in the Utilities section under Applications. As an alternative, you can rapidly look for and launch the app using Spotlight (type Cmd + Space and begin typing "Console").
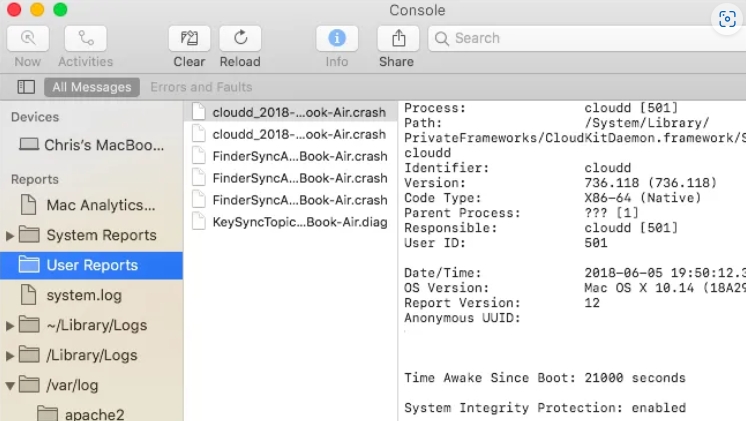
Step 2: Choose the System Log Source
A list of log sources can be seen in the Console app's left sidebar. These include diagnostic reports, application logs, system logs, and more. To examine the source's accompanying logs, click on the pertinent source.
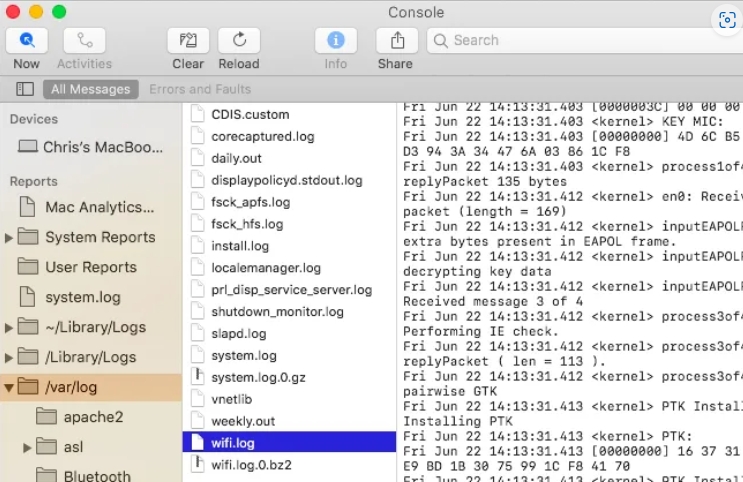
Step 3: Browse Logs
The Console app's center screen will show the entries for the selected log. To review events, scroll through the log entries. Time stamps, categories, and severity levels are used to arrange the logs.
- Navigating and Interpreting Logs:
- Timestamps: A timestamp is included in every log entry to show when the event took place. This aids in determining the order of occurrences.
- Categories and Filters: You may filter logs using the Console app's several categories, including Errors, Warnings, Information, and more. This makes it easier to concentrate on certain occurrences.
- Search functionality: To find particular terms, error codes, or phrases inside the logs, use the search box in the top-right corner.
- Details Pane: After selecting a log entry, the lower pane will show additional specific details about the occurrence. This frequently contains further background, error codes, and associated information.
- Exporting Logs: From the Console app, you may export logs as needed for additional analysis or sharing with support teams. Right-click on a log entry and choose "Export" to save the log to a file.
Part 3: MacOS Event Viewer: Gaining Insights
A consolidated platform for accessing and interpreting numerous system events and logs is offered by the MacOS Event Viewer. It compiles logs from several sources and enables you to examine them all at once, giving you a thorough understanding of your system's operations.
Using the Event Viewer:
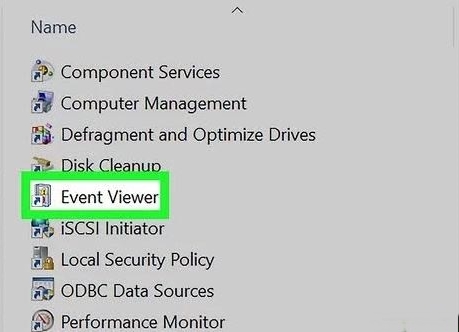
Step 1: Access Event Viewer
Launch the Event Viewer from the Applications > Utilities folder or by searching for it using Spotlight.
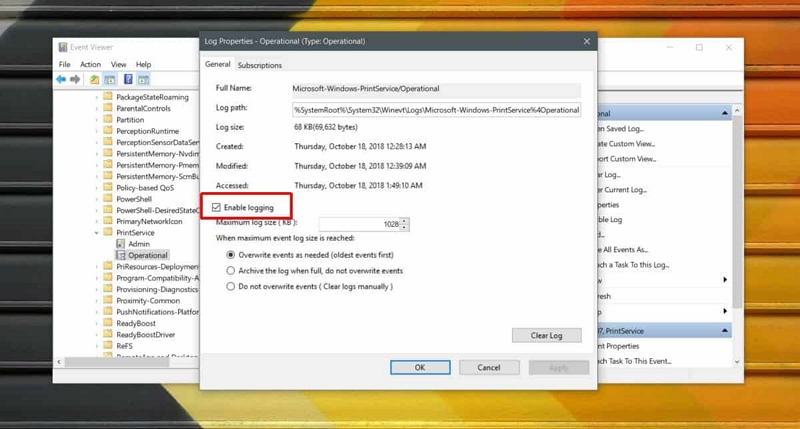
Step 2: Select Log Categories
The Event Viewer categorizes logs into sections such as Applications, System, Security, and more. Click on the relevant category to view logs.
Step 3: Time-Based Navigation
The Event Viewer enables you to filter logs based on specific time frames, making it easier to focus on recent events or occurrences during a particular period.
Step 4: Detailed Analysis
Click on individual log entries to access detailed information. The Event Viewer often provides contextual information, error descriptions, and suggestions for resolving issues.
Step 5: Correlation and Patterns
By examining logs from different categories together, you can identify correlations or patterns that might indicate underlying problems or areas for improvement. Keep in mind that knowing the different types of events that are logged and how they relate to the performance and health of the system is necessary for efficient use of the Event Viewer. It's an effective tool that can assist you in keeping track of the activity of your MacOS system.
Part 4: Digging Deeper: Advanced Techniques
1. Terminal Commands for System Log Retrieval
Terminal commands offer advanced users a more direct way to access system logs:
Step 1: Open Terminal
Launch the Terminal app from Applications > Utilities or by using Spotlight.
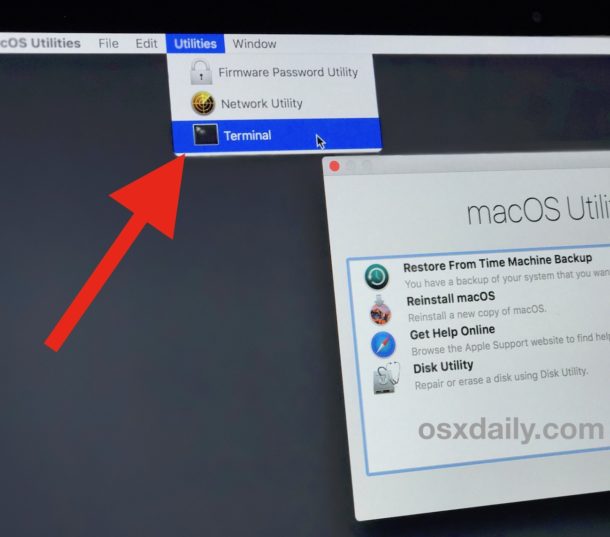
Step 2: View System Logs
Use the log command followed by options and parameters to retrieve specific logs. For example, log show --predicate "eventMessage contains 'error'" --style syslog
- Custom Filters: Terminal commands allow you to create custom filters to narrow down the log entries based on keywords, timeframes, or severity levels.
- Explore Log Commands: Use the man log command to access the manual pages and explore more options and syntax for retrieving logs.
Terminal commands provide a powerful way to access logs efficiently, but they require familiarity with command-line interfaces and log structures.
Part 5: Making Sense of the Logs
Deciphering System Log Entries:
- Comprehending Log Format: Timestamps, event kinds, source information, and error codes are all included in the standard format of system logs. Learn how to read logs in this format and interpret them correctly.
- Interpreting Error Codes: Log entries frequently include error codes. To learn about the significance of these codes and potential fixes, do some web research or consult official literature.
- Context Matters: Logs may contain contextual data that explains why an event happened. Be mindful of specifics like application names, user behaviors, and system conditions.
- Patterns and Anomalies: Examine the logs for any anomalies, recurring warnings, or patterns of failures that are similar. You can address fundamental issues by identifying reoccurring concerns.
Part 6: Troubleshooting and Solutions
Analyzing Logs for Troubleshooting:
- Identify Critical Errors: Pay close attention to logs that contain critical errors or warnings. These entries frequently offer hints as to what the underlying issue is.
- Sequence of Events: Analyze the events that led up to a problem in the sequence of events. Recognizing the sequence of events can assist in determining when the issue first appeared.
- Correlation: Compare logs from various sources, including system logs, security logs, and application logs. Relationships and dependencies can be discovered by correlating events from various sources.
- Google and Online Resources: Look for information and answers in online forums, government publications, or community resources when confronted with strange error codes or warnings.
Part 7: Keeping Your System Healthy
Regular Log Inspection for Maintenance:
Make it a habit to regularly monitor system logs, even when everything seems to be working as it should. You can prevent possible problems from getting worse by doing routine checks to find them early.
Conclusion:
System logs serve as a silent observer in the MacOS universe, recording each action and event that occurs within the operating system. They are an essential resource for identifying problems, ensuring system health, and comprehending the complex operations of your Mac.
You've developed a strong set of abilities by learning how to access, analyze, and use system logs. You can now successfully go through the internal workings of your Mac, fix issues, and maintain its performance. With your gained knowledge, you are better equipped to tackle problems with assurance, decide wisely, and improve your Mac experience. You're on a path to becoming a more knowledgeable and skilled user of technology as you continue to delve deeper through system logs. Also, to clean your Mac properly from junk files, logs, caches, and protect your privacy, use Macube for all time.
Hot Articles

Macube Cleaner
Speed up and troubleshoot your Mac super easily with a Macube full-featured free trial!
Start Free Trial