When your mouse pointer turns into a spinning wheel or an application window goes white, it's a sign that your app has crashed. In this state, the app is unresponsive, and you can't interact with it. It's crucial to address this issue immediately to prevent potential data loss and disruptions to your schedule.
Understanding the causes and solutions for unresponsive apps on a Mac can help you troubleshoot effectively and maintain your workflow.
Part 1: Reasons for Unresponsive Apps on a Mac
Resource Overload: When an application consumes too much memory or CPU power.
Software Bugs: Errors in the application's code can cause it to malfunction.
Compatibility Issues: Conflicts with the operating system or other installed software.
Malware: Viruses or malware can interfere with application performance.

Part 2: Solutions for Unresponsive Apps on a Mac
When an app becomes unresponsive or stops working, the quickest solution is to close or uninstall it. Your computer offers various methods to help you accomplish this. Keep reading to learn more about these solutions and how to implement them.
Method 1: Uninstall Malware Infection - Use Macube Cleaner
Sometimes software corruption or crashes can cause an app to become unresponsive. In such cases, the best course of action is to uninstall the software and reinstall it. For a comprehensive solution, Macube Cleaner is your ideal Mac companion. Macube Cleaner excels at removing duplicate files, junk files, malware, and more, ensuring a clean and optimized storage environment. This helps Mac users enjoy smoother performance and a better experience with all their apps.
Key Feature
- Uninstall software and all its associated files with just one click.
- Clean up junk files effortlessly to free up space for reinstalling software.
- Set custom criteria for scanning files, such as duplication and similarity.
- Advanced intelligent scanning function detects various file types, including photos, videos, PDFs, ZIP files, and more.
How to Uninstall Applications via Macube Cleaner
Step 1: Open Macube Cleaner and select the Uninstaller function. Then, click "Start".
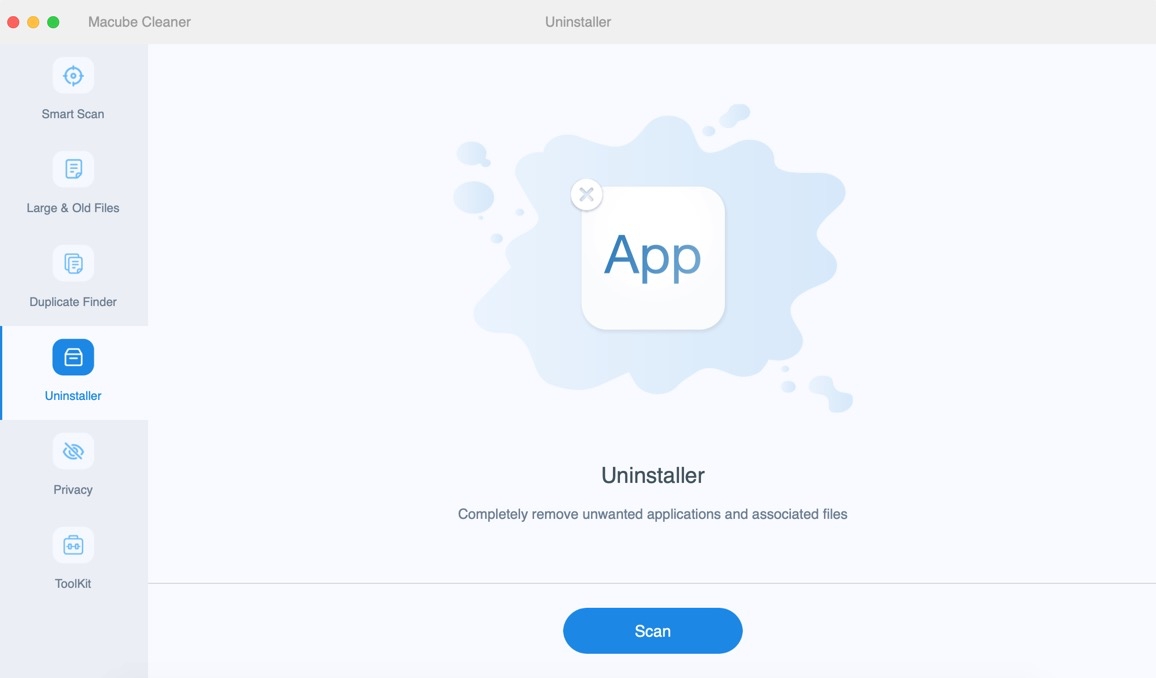
Step 2: Review the results and choose the unnecessary applications.
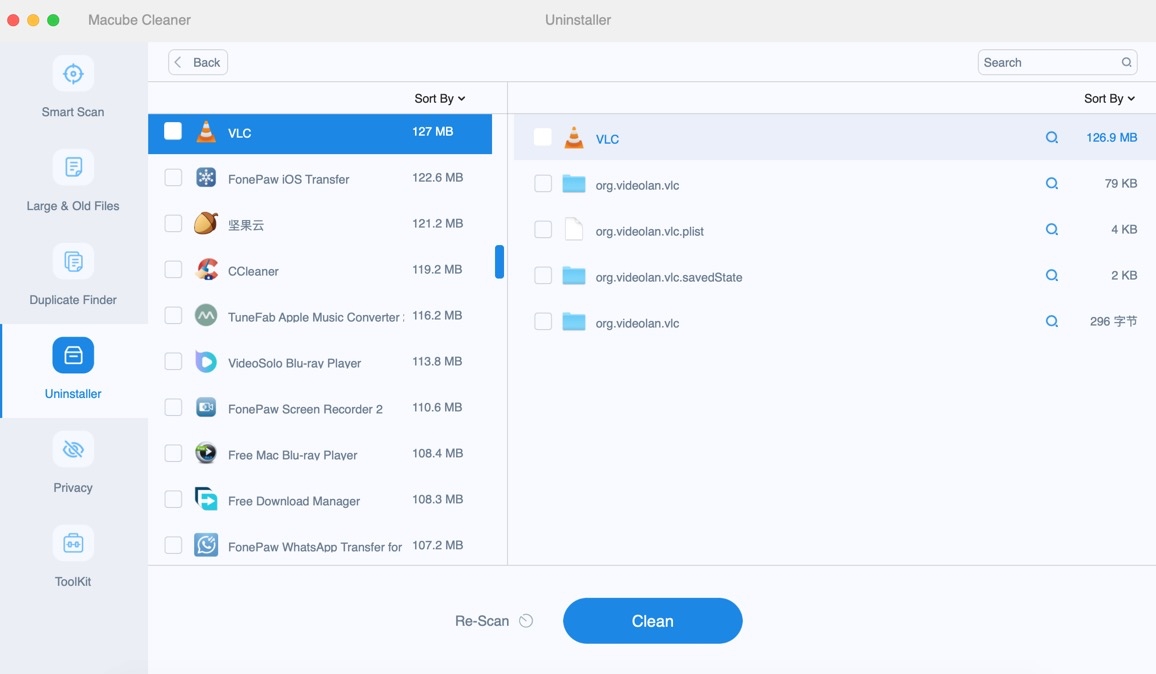
Step 3: Click Clean and Macube Cleaner will directly uninstall the software you have selected, including other files it hides.
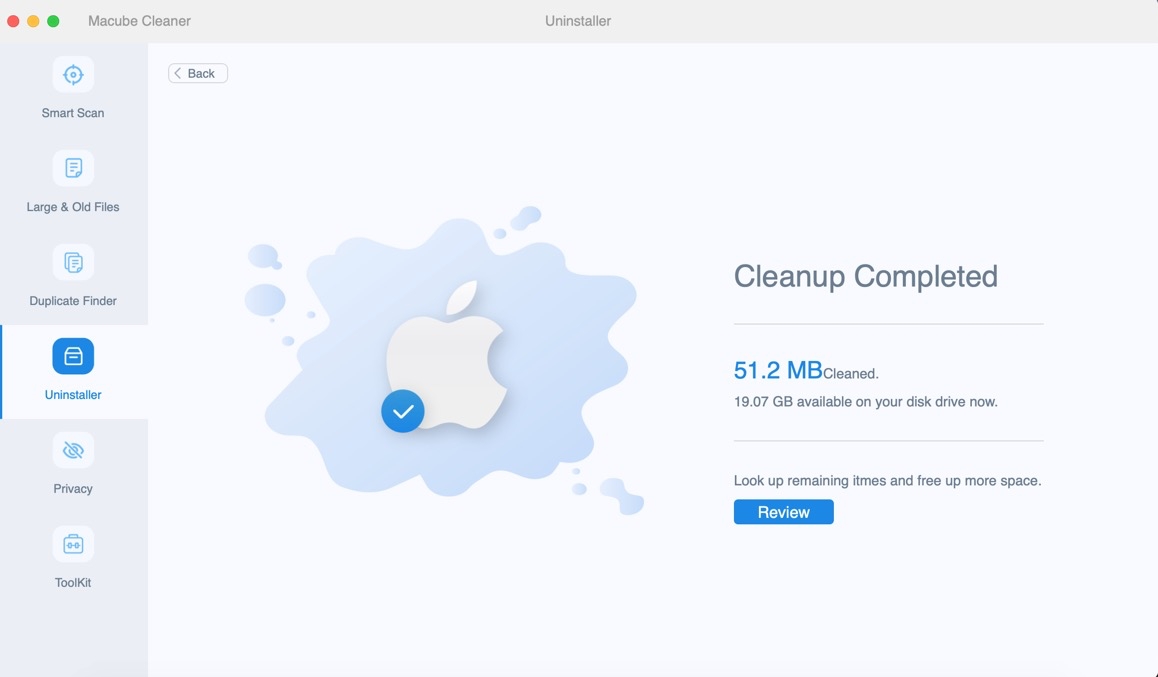
Afterward, head to the Apple Store to re-download and install the desired software. Software developers consistently check for bugs and release updates, ensuring that newly downloaded software is stable and less prone to crashes.
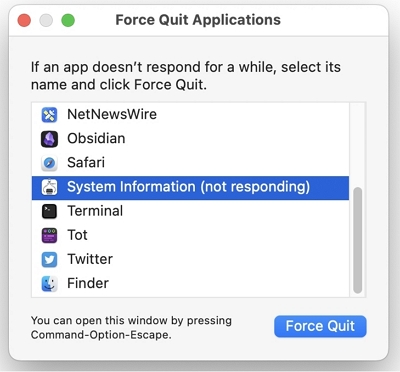
Method 2: Force Quit with Keyboard Shortcut: Command-Option-Escape
If your mouse is still responsive, you can access the Apple Menu and choose "Force Quit." However, if your mouse stops working, you can use the keyboard shortcut Command-Option-Escape.

This will bring up a system dialog box listing all active programs on your Mac. From there, select the unresponsive program and click "Force Quit" to close it.
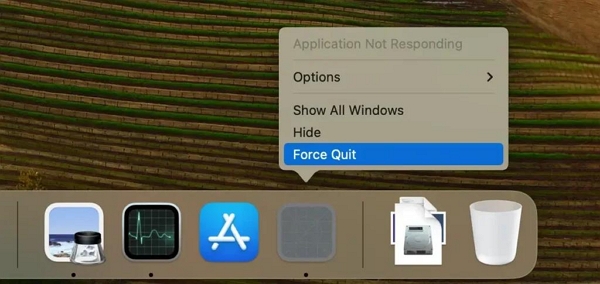
Method 3: Force Quit a Frozen App Using the Dock Icon
An alternative method to forcefully close a frozen application is by using the Force Quit feature on the desktop.
Step 1: Find the app's icon on the Dock.
Step 2: Right-click (or Control-click) the icon. Choose "Force Quit" from the menu.
Step 3: Confirm the action if prompted. Wait for the app to close.
Method 4: Force Quit a Hanging App Using Activity Monitor
To force quit a hanging application using the Activity Monitor:
Step 1: Open the Activity Monitor application, which can be found in the "Utilities" folder within the "Applications" directory.
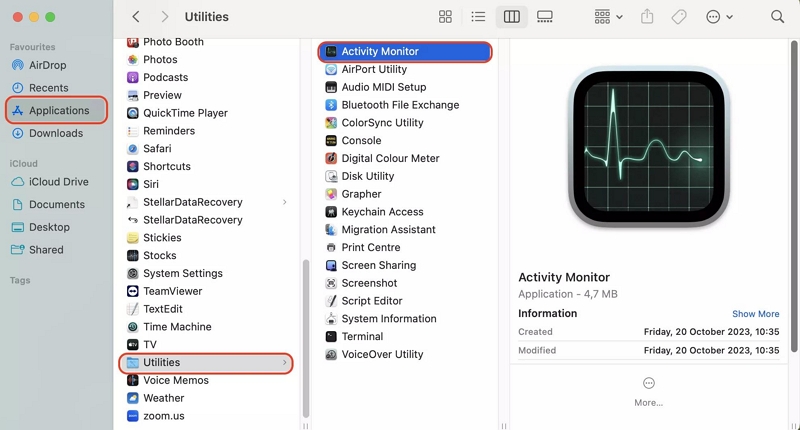
In the Activity Monitor window, you'll see a list of all running processes and applications. Look for the name of the unresponsive application. You can use the search bar at the top right corner to quickly locate it.
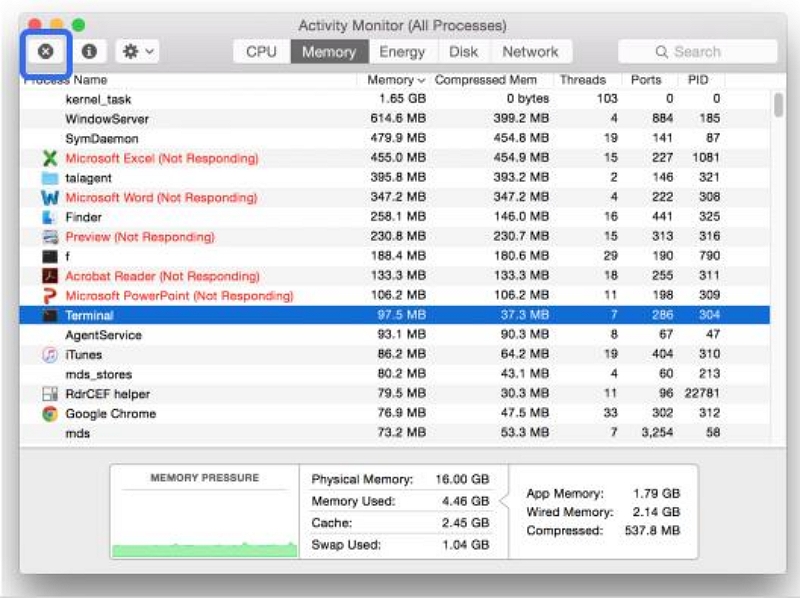
Step 2: Unresponsive applications are highlighted in red and labeled as "Not Responding" next to their names. Once you've identified the problematic application, select it from the list.
Step 3: With the unresponsive application selected, click on the "X" icon located in the top-left corner of the Activity Monitor window. This will prompt a confirmation dialog.
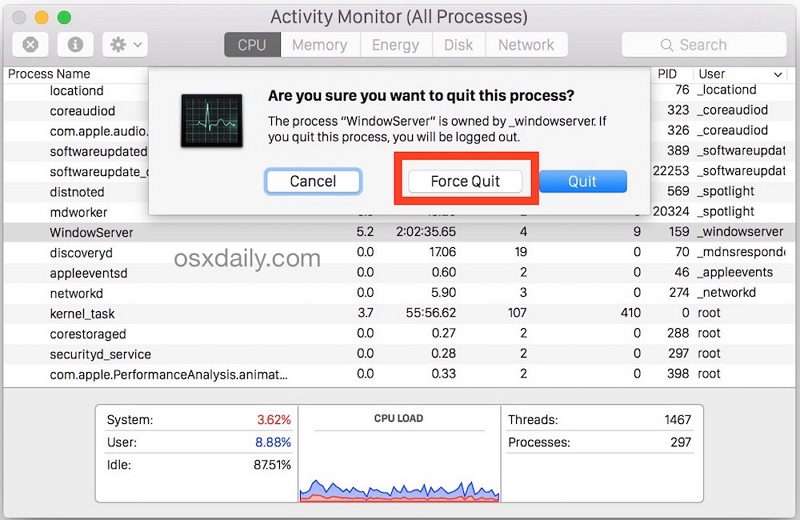
Step 4: Confirm that you want to force quit the application by clicking on the "Force Quit" button in the confirmation dialog.
Step 5: Wait for Activity Monitor to close the unresponsive application. Once it's done, you can close Activity Monitor itself.
Method 5: Force Quit a Hanging App from the Terminal Command Line
To force quit a hanging app from the Terminal command line, you're essentially using a command-line interface to achieve what you would normally do through the graphical user interface (GUI). This method can be useful if you prefer using the command line or if the GUI is unresponsive.
Step 1: Open the Terminal application, which you can find in the "Utilities" folder within the "Applications" directory.
Step 2: In Terminal, type the following command to force quit the application: killall [appname]

Step 3: Replace [appname] with the name of the application you want to quit. For example, to force quit Stream, you would type: killall Stream

Step 4: If the application name contains spaces, enclose it in quotes. For example, to force quit System Information, type: killall "System Information"

Step 5: Press the Return or Enter key on your keyboard. macOS will then force quit the specified application.
By using these steps, you can effectively force quit a hanging application from the Terminal command line on your Mac.
Method 6: Delete Application Preference Files (plist Files)
Deleting application preference files (plist files) is a troubleshooting step that can help resolve issues with misbehaving or unresponsive applications on your Mac. These plist files store various settings and preferences for applications, and sometimes they can become corrupted, causing the app to malfunction. Deleting these files forces the application to create new, default settings files, which can often resolve the issue.
Step 1: Ensure the application you are troubleshooting is closed before you proceed. Click on the Finder icon in the Dock to open a Finder window.
Step 2: In the Finder menu bar, click on "Go" and then select "Go to Folder..." Alternatively, you can press Shift-Command-G.

Step 3: In the "Go to Folder" dialog box, type ~/Library/Preferences and press Enter. This will take you to the Preferences folder within your user library.

Step 4: In the Preferences folder, look for the plist file that corresponds to the application you're troubleshooting. The file name usually includes the application's name or the developer's name. For example, the preference file for the application "Stream" might be named com.stream.app.plist
Step 5: Once you find the correct plist file, right-click on it and select "Move to Trash." Alternatively, you can drag the file to the Trash.
Step 6: Open the application again. It will generate a new plist file with default settings, which can often resolve any issues you were experiencing.
 Important Notes
Important Notes
- Before you delete a plist file, it's wise to back it up. This way, you can restore it if needed. Simply copy the file to another location on your computer.
- Deleting a plist file will revert the application’s settings to their default state. Be prepared to reconfigure your settings within the app afterward.
Method 7: Try Apple Diagnostics or Apple Hardware Test
Apple Diagnostics is a built-in tool for newer Mac models (post-June 2013) that tests hardware for problems.
How to Use Apple Diagnostics:
Step 1: Disconnect all external devices except the keyboard, mouse, display, and Ethernet connection. Ensure your Mac is on a flat, stable surface.
Step 2: Shut down your Mac. Turn it on and immediately hold down the "D" key. Release the key when the language selection screen appears. (For some Macs, hold Option-D instead.)
Step 3: The test will start automatically and take a few minutes. After completing, it will display any found issues along with reference codes.
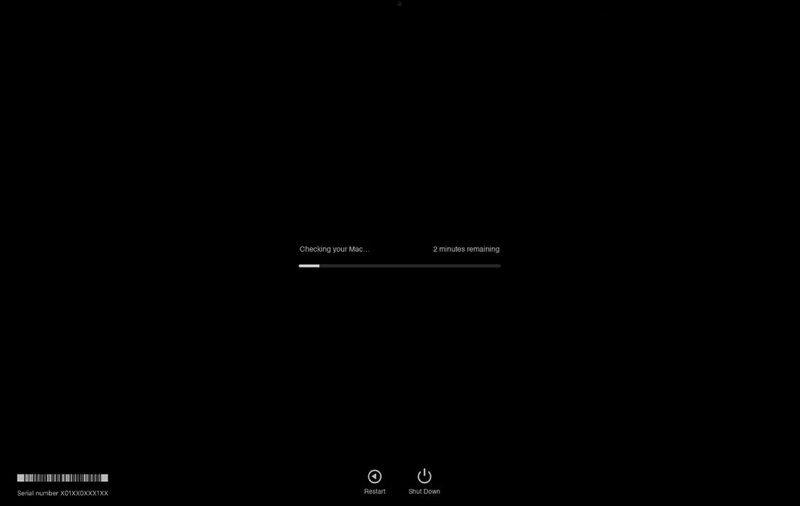
Step 4: Note the reference codes for troubleshooting or when contacting Apple Support. Follow any on-screen instructions.
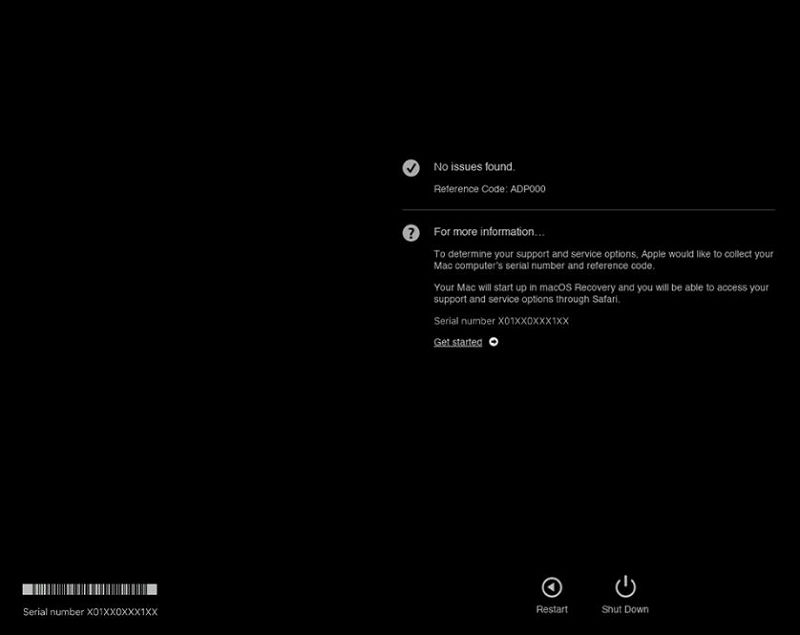
Apple Hardware Test is for older Mac models (pre-June 2013) and functions similarly to Apple Diagnostics.
How to Use Apple Hardware Test:
Step 1: Disconnect all external devices except the keyboard, mouse, display, and Ethernet connection. Ensure your Mac is on a flat, stable surface.
Step 2: Shut down your Mac. Turn it on and immediately hold down the "D" key. Continue holding until the Apple Hardware Test icon or language selection screen appears. (For some Macs, hold Option-D instead.)
Step 3: Select your language and press Return. Click "Test" or press "T" to begin. For a more thorough test, check the extended test option.
Step 4: Review any displayed error codes. Note these codes for troubleshooting or when contacting Apple Support. Follow any on-screen instructions. Having the reference codes ready will be helpful when seeking assistance from Apple Support.
Method 8: Boot Your Mac in Safe Mode
Booting your Mac in Safe Mode can help troubleshoot various issues. Here’s what Safe Mode does:
1. Disables Third-Party Extensions: Stops third-party kernel extensions from loading.
2. Verifies Startup Disk: Checks and attempts to repair any issues on your startup disk.
3. Disables Startup Items: Prevents startup and login items from launching automatically.
4. Clears Caches: Deletes font caches, the dynamic loader cache, and other system caches.
Step 1: Ensure your Mac is completely powered off.
For Intel-based Macs: Turn on your Mac and immediately press and hold the Shift key. Release the Shift key when you see the login window.
For Apple Silicon (M1 or later) Macs:
- Turn on your Mac and continue to hold the power button until you see the startup options window. Select your startup disk.
- Press and hold the Shift key, then click "Continue in Safe Mode." Then, release the Shift key.
![]()
Step 2: Log in to your Mac. You might be asked to log in twice if FileVault is enabled.
Step 3: You’ll see "Safe Boot" in the menu bar on the login screen. You should then open the malfunctioning application. If it still crashes, the application itself is to blame. I'm afraid you'll have to download and reinstall the program to try it. To uninstall the failed application, skip to Method 1.
 Note:
Note:
- Simply restart your Mac without holding any keys to exit Safe Mode and boot normally.<
Part 3: Can Unsaved Work Be Recovered If an Application Becomes Unresponsive and Needs to Be Force Quit?
When an application becomes unresponsive on a Mac, you may lose unsaved work if you have to force quit it. However, there are a few ways you can try to recover your unsaved work:
Way 1. Check the application's autosave feature
Many applications on Mac have an autosave feature that periodically saves your work automatically. Check the application's preferences or documentation to see if it has an autosave feature and where the autosaved files are stored.
Way 2. Look for temporary files
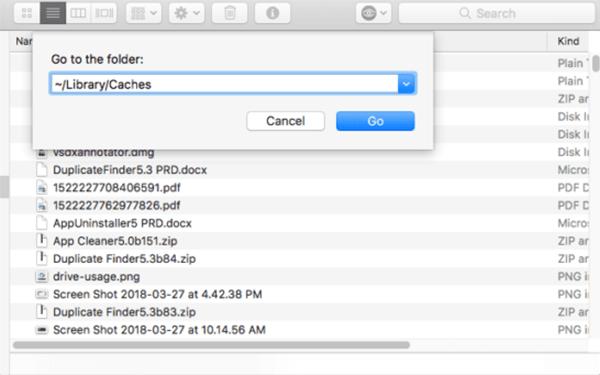
Some applications create temporary files while you're working on a document. These files may contain unsaved changes. Click on the Finder icon in the Dock. From the Finder menu, select "Go" > "Go to Folder." Type ~/Library/Caches/ and press Enter. In the window that opens, look for any temporary files that might contain your unsaved work.
Way 3. Use data recovery software:
If you can't find any auto saved or temporary files, you can try Eassiy Data Recover Software to scan your Mac's hard drive for deleted or corrupted files. There are several data recovery software options available, both free and paid.
Remember, the best way to protect your work is to save it frequently. Regularly pressing Command + S or using the application's "Save" command can help prevent data loss in case of unexpected application crashes or force quits.
Conclusion:
By following the solutions provided above, you can effectively resolve issues such as program crashes or unresponsiveness on your Mac. Whether you opt for the convenient Macube Cleaner or manually force quit applications, you'll be able to restore functionality and resume using the software. Moreover, regularly cleaning up junk files on your Mac ensures sufficient space for smooth software operation, enhancing overall system performance.

Macube Cleaner
Speed up and troubleshoot your Mac super easily with a Macube full-featured free trial!
Start Free Trial